What is climate risk?
Climate risk refers to the potential negative effects of climate change on aspects of the environment, businesses, and society. Rising global temperatures can change the climate system and the components within it. This change affects the Earth’s weather and climate patterns. As a result, the globe is experiencing more frequent and severe extreme weather events.
An increase in extreme weather events
An increase in extreme weather events correlates to agricultural production impacts. Drought, flood, convective storms (hail and wind damage), and tropical cyclones have been increasing for decades. Recently, these increases have been accelerating.
The economic cost of climate-related weather event
In 2024, the US had 27 weather and climate disasters defined as losses at, or over, 1 billion dollars (SOURCE: NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information). This was the second-largest number of billion-dollar events only being surpasses by 28 events in 2023.
In 2024, 58 billion-dollar weather disasters globally caused US $402 billion in economic loss (SOURCE: Gallagher Re). Much of this loss was in the agricultural sector. This was the second-highest number of disasters, with the record set in 2023. The three biggest weather disasters in 2024 were Hurricane Helene, Hurricane Milton, and flooding in central China. These events had a significant impact on the economics of the areas impacted, and the world.
Climate risk: The enemy of crops
The ranking of the top hazards tells us much about the agricultural impacts. Tropical cyclones, floods, severe convective storms (hail and wind), and drought contributed the most economic loss. Of course, these are the enemies of crops.

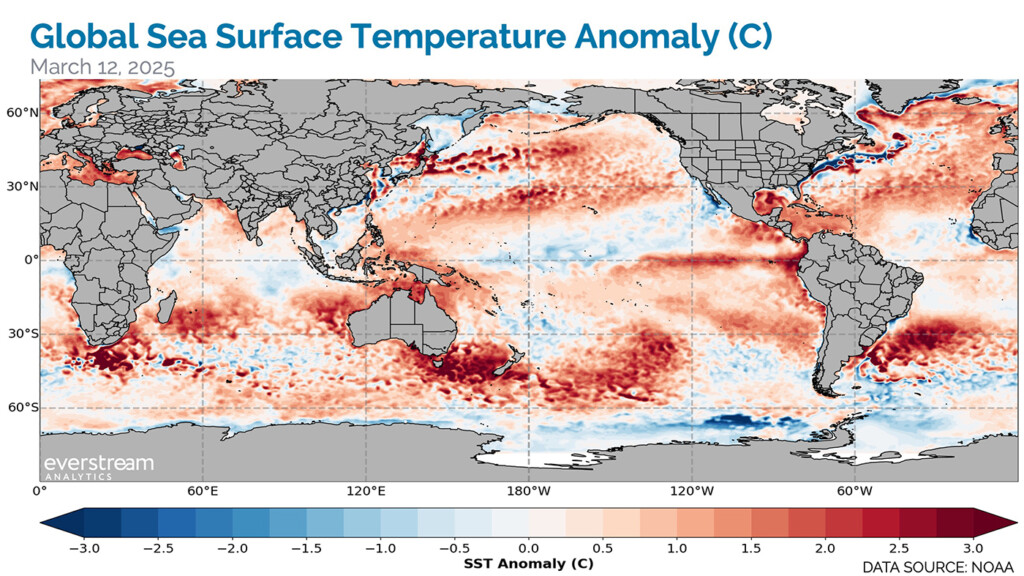
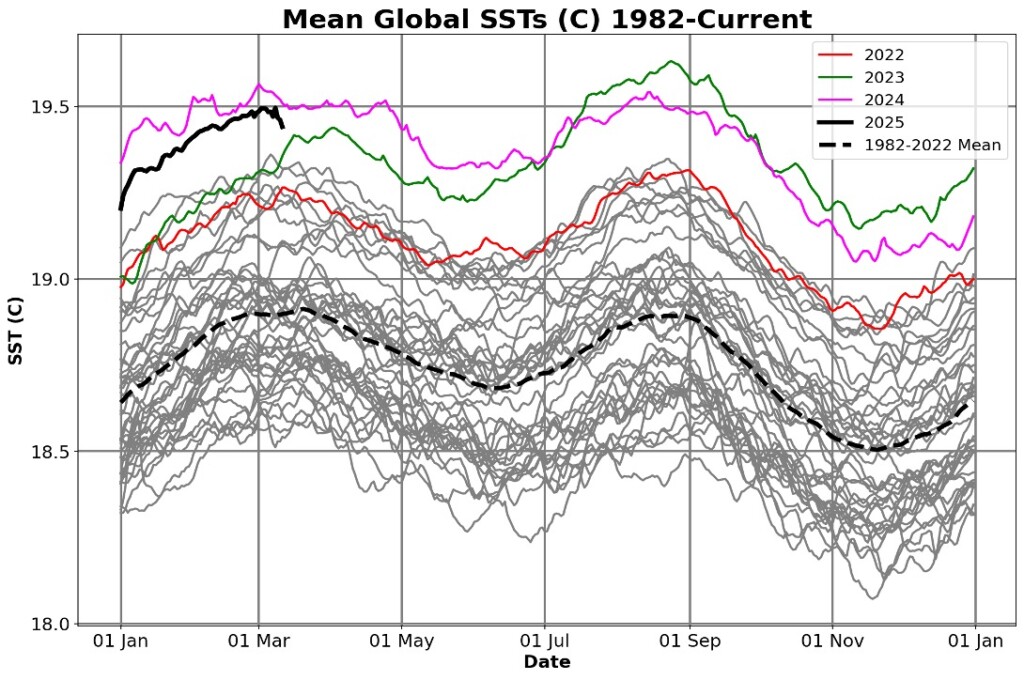 Figure 1: Global sea surface temperature (SSTs) trends that contribute to increased climate risk
Figure 1: Global sea surface temperature (SSTs) trends that contribute to increased climate risk