Furthermore, tariffs can cause supply chain disruptions, as companies seek alternative suppliers or relocate production to mitigate trade risks. However, changing the flow of a supply chain can be time-intensive and costly, especially if a company is acting reactively and under pressure. Supplier changes may be further delayed due to device manufacturer requirements to obtain regulatory agency approvals of supplier changes.
Finally, the cost and operational burden can have a ripple effect through the rest of the company. Medical device manufacturers may be forced to reallocate budgets due to increased costs, delaying or scaling back key research and development initiatives that could lead to new and improved medical technologies. Given these challenges, companies must develop strategic approaches to mitigate tariff-related risks, ensuring ongoing access to medical devices and continual innovation within the sector, without compromising affordability and quality.
Key tariffs
Trade regulations and tariffs are constantly changing. Countries that impose tariffs may find themselves facing retaliatory tariffs, creating complex and expensive issues within medical device supply chains. However, there are a few key trade disputes and tensions that are worth noting as you create your supply chain risk mitigation plans.
The US-China trade war had led to extensive tariffs on medical device components and finished products. The US first announced increased tariffs in 2024 on some Chinese imports including syringes and needles, battery parts, semiconductors, respirators, and certain critical minerals and permanent magnets vital to medical device manufacturing under Section 301 of the Trade Act. Under an executive order, an additional 10% tariff was imposed on all Chinese goods from February 1, with this rate increased to 20% from March 4. These tensions seem unlikely to soften soon, and so it’s worth considering this geopolitical relationship in your long-term strategy.
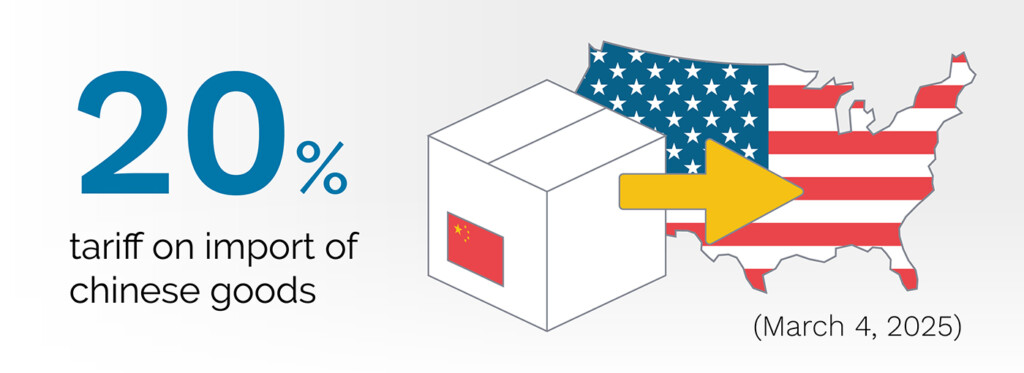 Figure 1: U.S. Tariff Rate on Chinese Imports: 20% Effective March 4, 2025
Figure 1: U.S. Tariff Rate on Chinese Imports: 20% Effective March 4, 2025
The US has also extended 25% tariffs on imports from Canada and Mexico using authority under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA). While these tariffs have been temporarily paused for items compliant with the USMCA free trade agreement, they threaten to provoke a trade war on the continent, with Canada already implementing a first set of retaliatory tariffs. Disruptions to trade with Mexico could prove particularly impactful to medical device manufacturers, many of whom have established operations in the country.
The European Union has also imposed a series of complex regulations, including the Medical Device Regulation and import duties on certain medical goods. This has made it more expensive and time-consuming for companies to bring products to the European market. Furthermore, Brexit has created new trade barriers between the UK and the EU, further complicating operations in the region, increasing customs costs and logistical delays for medical device shipments.
Creating proactive strategies
As tariffs continue to disrupt the medical device industry, companies must implement proactive strategies to minimize financial strain and maintain supply chain stability.
Diversifying the supplier base is one of the most effective ways to reduce tariff exposure. By sourcing raw materials and components from multiple regions, companies can avoid over-reliance on any single country affected by trade restrictions. Expanding supplier networks across different markets also enhances resilience, ensuring that production continues even in the face of sudden geopolitical changes.
Furthermore, onshoring and nearshoring, where possible, can also be an effective strategy to minimize tariff risks. Moving production closer to primary markets allows manufacturers to have greater control over sourcing, production, and shipping, all while minimizing tariff exposure. Both strategies, however, can be time and cost intensive during their set up, though they may ultimately pay dividends.
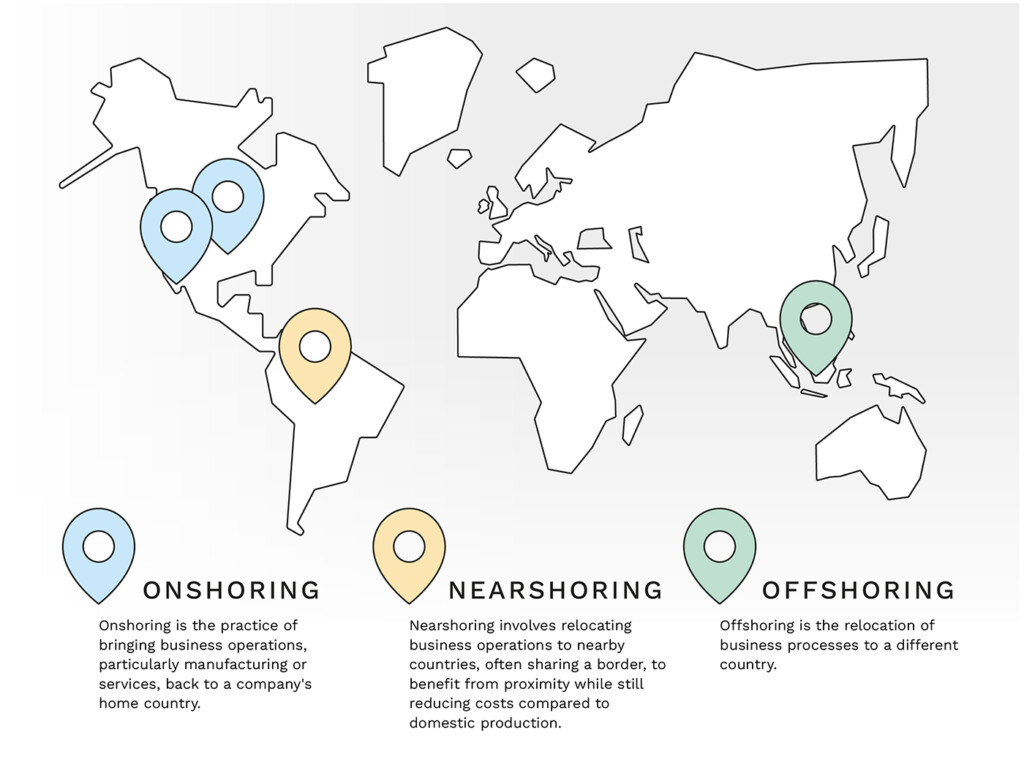 Figure 2: Understanding global sourcing: Nearshoring, Onshoring, and Offshoring
Figure 2: Understanding global sourcing: Nearshoring, Onshoring, and Offshoring
Finally, investing in advocacy and policy engagement can play a critical role in mitigating tariff impact. By working with industry groups, trade associations, and government officials, medical device companies can push for tariff exemptions, renegotiation of trade policies, and more favorable regulatory framework. Staying informed on evolving trade agreements and actively participating in policy discussions ensures that businesses have a voice in shaping the trade decisions that directly impact their supply chains.
Next steps
A long journey starts with the first few steps. Your company and sector won’t be able to address all of these supply chain risks overnight, especially in the face of a constantly changing landscape. Start by making sure you fully understand how and where your supply chain functions, from your Tier-1 vendors to all of your sub-tier suppliers. This knowledge will help you see where your potential areas of over-dependency – and therefore risk – are.
Then, invest in tools to help you continuously monitor for tariff changes, and other factors that may impact your supply chain. AI-powered solutions like Everstream Explore can give you advanced notice of upcoming decisions, allowing you to make proactive decisions.
Finally, be prepared to make quick shifts, if necessary. Check out and engage alternative suppliers, so any changes are handled as efficiently as possible in the face of critical situations.
Tariffs pose significant challenges for the medical device industry. From rising production costs to supply chain disruptions, the impact can be far-reaching and dangerous for healthcare providers and patients. Creating a proactive strategy to mitigate risks can go a long way to ensuring supply chain stability, ensuring that patents around the world are able to access essential medical technologies.

 Figure 1: U.S. Tariff Rate on Chinese Imports: 20% Effective March 4, 2025
Figure 1: U.S. Tariff Rate on Chinese Imports: 20% Effective March 4, 2025  Figure 2: Understanding global sourcing: Nearshoring, Onshoring, and Offshoring
Figure 2: Understanding global sourcing: Nearshoring, Onshoring, and Offshoring