Financial sanctions, trade restrictions, production stoppages, and airspace shutdowns are disrupting the global supply chain as the Ukrainian-Russian war continues. Here we share our intelligence team’s insights to help companies shift logistics and procurement operations to keep their workers safe, to lighten loads on overwhelmed borders, and to respect and follow fast-moving sanctions.
Sanctions targeting access to international financial system
Sanctions on several Russian banks include restricting access to U.S. dollar transactions, freezing assets, and removal from the SWIFT financial messaging system. However, the U.S. provided broad exemptions purchases of crude oil, natural gas and fuel to minimize disruption of energy markets.
Cutting access to Russia’s foreign currency reserves limits the Russian Central Bank in influencing the ruble’s exchange rate, with a weaker ruble likely leading to higher prices for imports into Russia, increasing inflation.
No sanctions have been imposed on key Russian commodities, but prices are still expected to increase. Metals supply might be tightened by market participants self-limiting due to increasingly restrictive sanctions.
U.S., UK, and EU restrict exports of key technology
Russia purchases about 70% of its chip supply from China, mostly low-end chipsets for use in automotive and home appliances. With new restrictions, Russia’s military will effectively be denied access to high-end semiconductors and other critical technology imports for its military applications.
Other prohibitions apply to telecommunication, encryption security, lasers, sensors, navigation, avionics, and maritime technologies, as well as more than 45 specific Russian companies active in the defense, aerospace, and shipbuilding sectors.
The EU has imposed a ban on the sale, supply, transfer, or export to Russia of technologies in oil refining, of aircraft and aircraft parts, and of dual-use goods and technology, including semiconductors. The UK has adopted similar prohibitions.
Production stoppages increasing across all industries
Many companies stockpiled parts and raw materials over the past few months, but still feel the effects of Ukraine production line shutdowns. Everstream Analytics has tracked more than 35 companies that have halted production operations across Ukraine and Russia, with most in consumer goods and automotive such as Leoni Wiring Systems, Sumitomo Electric Industries, and Henkel AG.
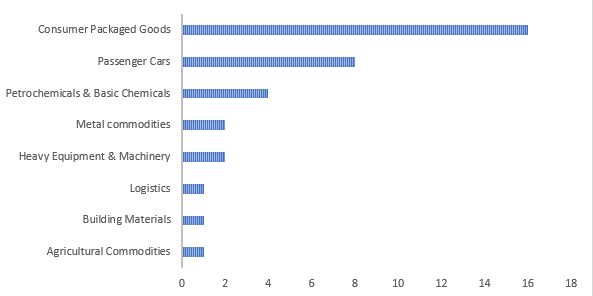
Global steelmakers, including Nippon Steel Corp and Voestalpine AG, scrambled for alternatives as key suppliers of iron-ore pellets such as Ferrexpo PLC were unable to export Ukraine cargoes. Biotech and pharma companies also face disruptions to more than 200 ongoing clinical trials in Ukraine, with some already warning of delays due to the military conflict.
Airspace bans could cause delays, higher costs for air cargo
Airspace closures could increase the cost of flying cargo from Europe to Asia, potentially leading to delays and even making some routes commercially unviable. Most airlines have been re-routing airplanes via the Middle East.
Several freight forwarders, including DSV, UPS, and FedEx, and express couriers have already suspended operations to and from Ukraine.
Ocean carriers are diverting cargo to alternative ports along the Black Sea and beyond, and rail connections from China to Europe will be affected. For example, freight forwarder Flexport Inc. stopped accepting bookings for its Asia-to-Europe freight rail service that runs through Russia.
What to watch out for in the coming days: volatile commodities and cyber attacks
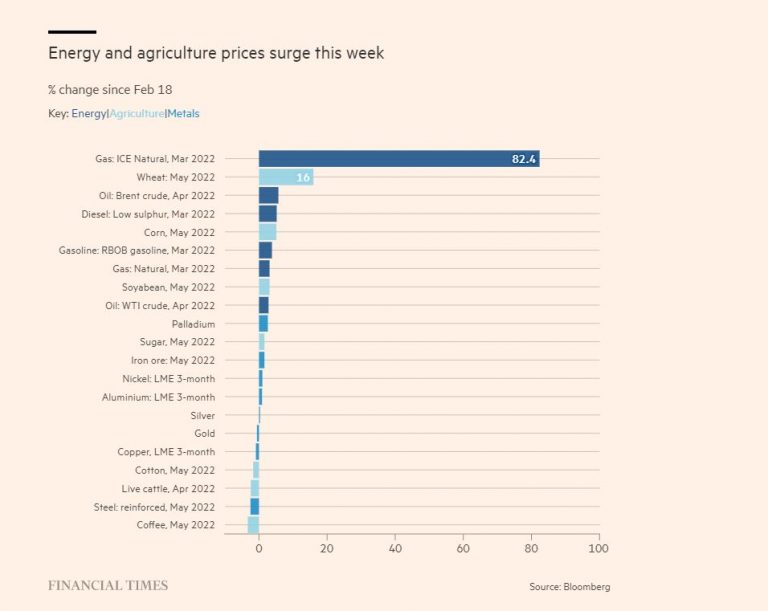
Commodity prices from oil and gas to metals and agriculture are likely to remain volatile and continue their upward trend of the past few months. Natural gas and crude oil as well as wheat and corn have experienced the biggest price increases last week compared to the week prior.
Companies with global supply chains should also brace for more cyberattacks in retaliation to the growing number of sanctions against Russia. For example, on early February 28, reports emerged of a cyber attack on Kojima Industries Corp, a key parts supplier to Toyota Motor Corp, which will force the carmaker to shut down all of its 14 production sites in Japan on March 1 (it was not immediately clear whether the cyber incident was directly connected to the ongoing situation in Ukraine and Russia).
What to do next
Steps that supply chain managers should be taking today:
- Consider activating contingency plans.
- Identify key suppliers or strategic logistics locations in Ukraine and Russia.
- Contact critical suppliers to assess the impact of the military conflict and the sanctions on their operations.
- Anticipate further volatility in commodity markets, growing supply shortages, and potential retaliatory cyber-attacks amid further sanctions that could be announced.
While many companies may not have direct Tier-1 suppliers in the conflict area, the possibility remains that key suppliers may be relying on inputs from Tier-2 or Tier-3 suppliers in Ukraine and Russia, which could be affected either by the ongoing military operations in Ukraine or the reciprocal sanctions between Russia and other countries.